Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
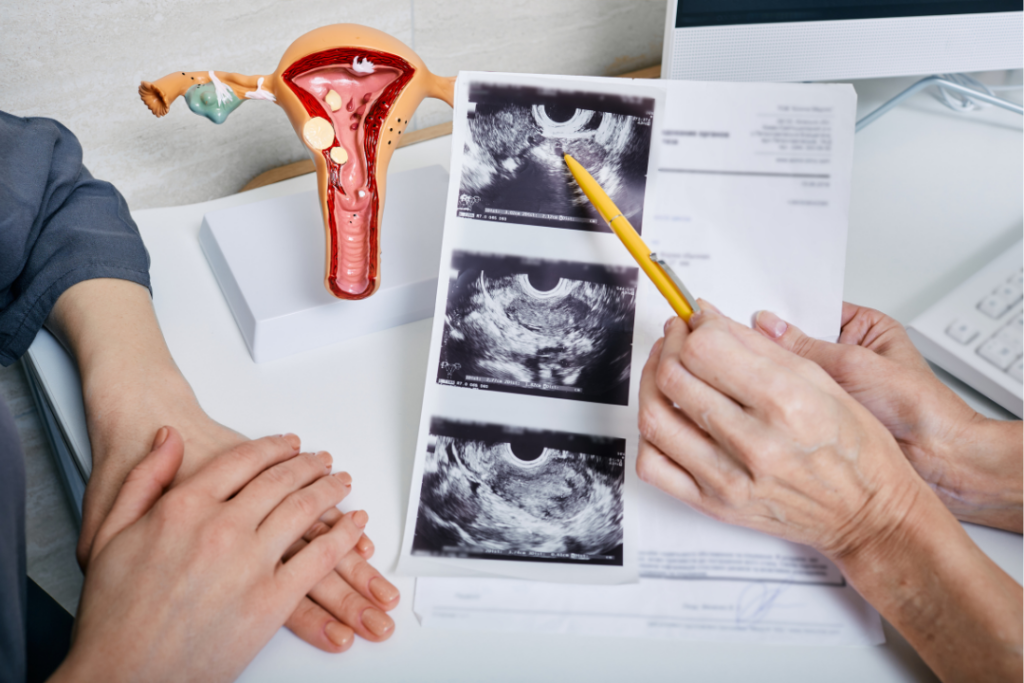
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a common hormonal disorder affecting individuals with ovaries. It is characterized by an imbalance in reproductive hormones that can lead to a variety of symptoms and health issues.
- Hormonal Imbalance
In PCOS, the ovaries often produce higher-than-normal levels of androgens (male hormones), which can disrupt the regular release of eggs and lead to irregular menstrual cycles or even absent periods. This hormonal imbalance can also contribute to symptoms like excessive hair growth (hirsutism), acne, and oily skin. - Ovarian Cysts
The term “polycystic” refers to the presence of multiple small cysts on the ovaries. These cysts are not usually harmful but can be associated with the hormonal imbalance and contribute to irregular periods and fertility issues.
- Metabolic Issues
PCOS is often linked with insulin resistance, where the body’s cells do not respond properly to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. This can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. Individuals with PCOS may also experience weight gain and difficulty losing weight. - Reproductive Health
PCOS can affect fertility by disrupting the normal ovulation process. It is a leading cause of infertility due to irregular ovulation. However, with appropriate treatment and lifestyle changes, many individuals with PCOS can conceive successfully.
Diagnosis and Management
Diagnosis of PCOS typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests to check hormone levels, and imaging studies like ultrasound to detect ovarian cysts. Management often includes lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, medications to regulate menstrual cycles, control symptoms like acne and hair growth, and address insulin resistance. Fertility treatments may be considered for those trying to conceive.
With proper management, individuals with PCOS can effectively control symptoms and reduce the risk of associated health conditions, leading to improved overall well-being.
